Understanding the Intricacies of Continuously Variable Transmission
Innovation in the automotive industry is a constant, with manufacturers pushing boundaries to provide smoother, more efficient driving experiences. One such innovation that continues to evolve is the Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT). The concept of a Continuously Variable Transmission isn’t a new phenomenon in the automotive sphere. Its origins can be traced back to Leonardo da Vinci, who drafted designs for a stepless continuously variable transmission in the 15th century. However, it wasn't until the 20th century that automobile manufacturers began incorporating this technology into their vehicles, with DAF, a Dutch automaker, leading the way. The CVT was a revolutionary idea, promising a seamless shift through an infinite number of effective gear ratios. This contrasted sharply with conventional transmissions, which offered a fixed number of gear ratios.
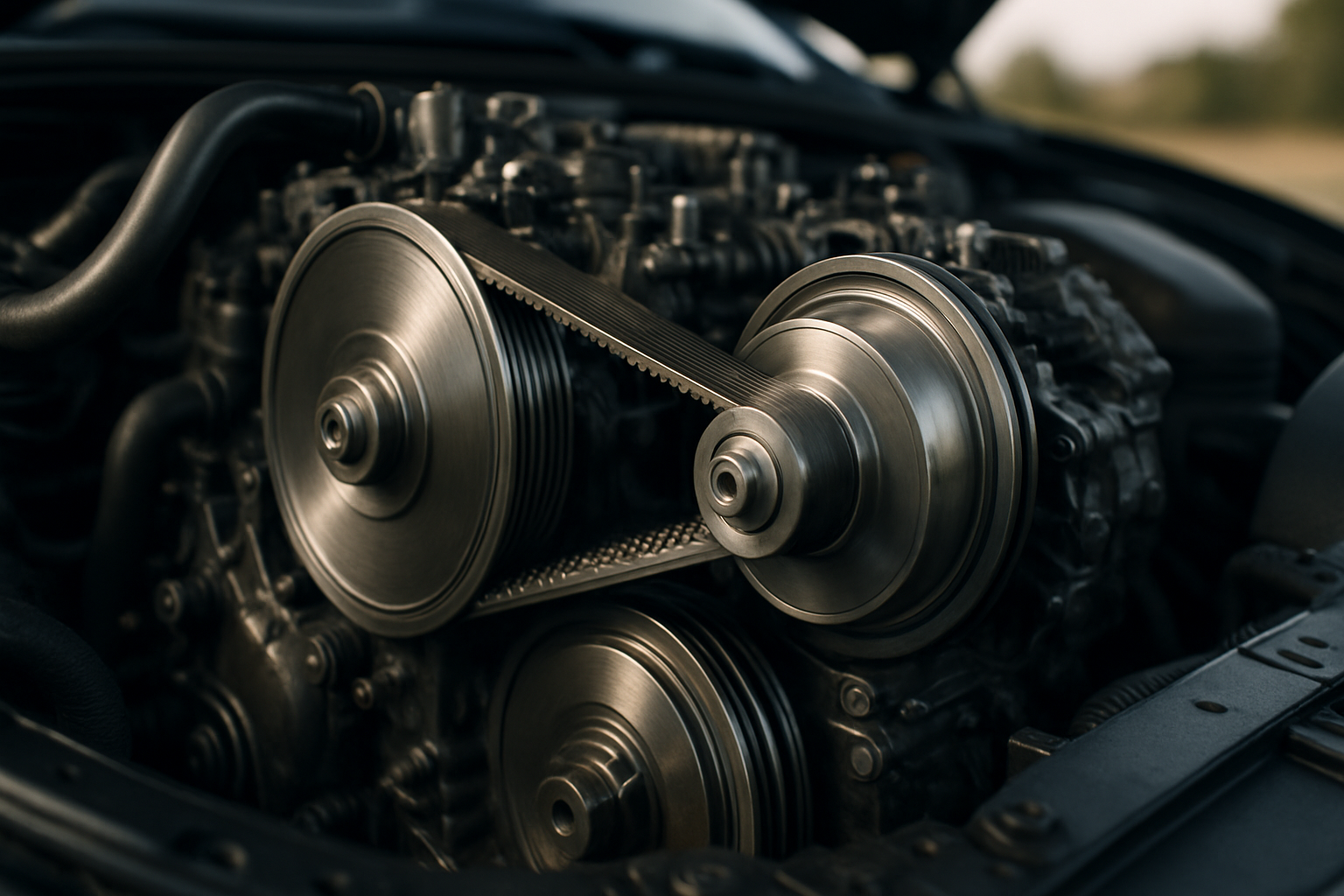
The Mechanics of a CVT
A CVT operates differently than traditional automatic or manual transmissions. It uses two pulleys connected by a belt, instead of gears, to transmit engine power to the wheels. One pulley is connected to the engine (input shaft), while the other sends power to the wheels (output shaft). The diameters of these pulleys can change based on the engine’s need, providing an infinite number of gear ratios. This variable gear ratio is what provides a smoother and more efficient driving experience.
The Impact of CVT on Today’s Auto Industry
CVTs have become an integral part of the modern automotive industry. They are particularly prevalent in compact cars and crossovers from manufacturers like Nissan, Honda, and Subaru. The main reasons for their popularity are their fuel efficiency and simplicity of operation. CVTs provide better fuel economy than traditional automatic transmissions by keeping the engine in its optimal power range. They also deliver a smoother ride, free of the “gear hunting” associated with traditional transmissions.
The Challenges and Benefits of CVTs
Despite the numerous benefits, CVTs have their share of challenges. The primary concern is their longevity, as CVTs have been known to be less durable over time compared to their conventional counterparts. However, advances in technology have steadily improved their resilience and lifespan.
On the upside, CVTs offer a smoother driving experience with improved acceleration and enhanced fuel efficiency. Their stepless operation allows the engine to run at its most efficient speed, regardless of whether the car is running at full throttle or cruising. This leads to better fuel economy, a significant advantage in today’s eco-conscious world.
Looking Forward: The Future of CVTs
The future of CVTs looks promising. Manufacturers continue to refine and enhance this technology, with a focus on improving durability and driver engagement. Some automakers are introducing artificial ‘stepped’ gear ratios to make CVTs feel more like traditional transmissions. Moreover, the push for greater fuel efficiency and smoother ride quality will likely keep CVTs relevant in the years to come.
The journey of the Continuously Variable Transmission from Leonardo da Vinci’s notebook to modern vehicles is a testament to the automotive industry’s relentless pursuit of innovation. As CVTs continue to evolve, they carry the potential to redefine efficiency and smoothness in our everyday drive.