The Manufacturing Process of Automotive Components
The automotive industry relies on a sophisticated and precise manufacturing process to create the myriad components that constitute a modern vehicle. From the smallest fastener to complex engine blocks and intricate electronic systems, each part undergoes rigorous design, production, and quality control. Understanding this intricate journey provides insight into the engineering marvels that underpin global mobility, driving the performance, safety, and efficiency we expect from vehicles on our roads today. The journey of an automotive component begins long before it is assembled into a car, involving a blend of traditional craftsmanship and cutting-edge technology.
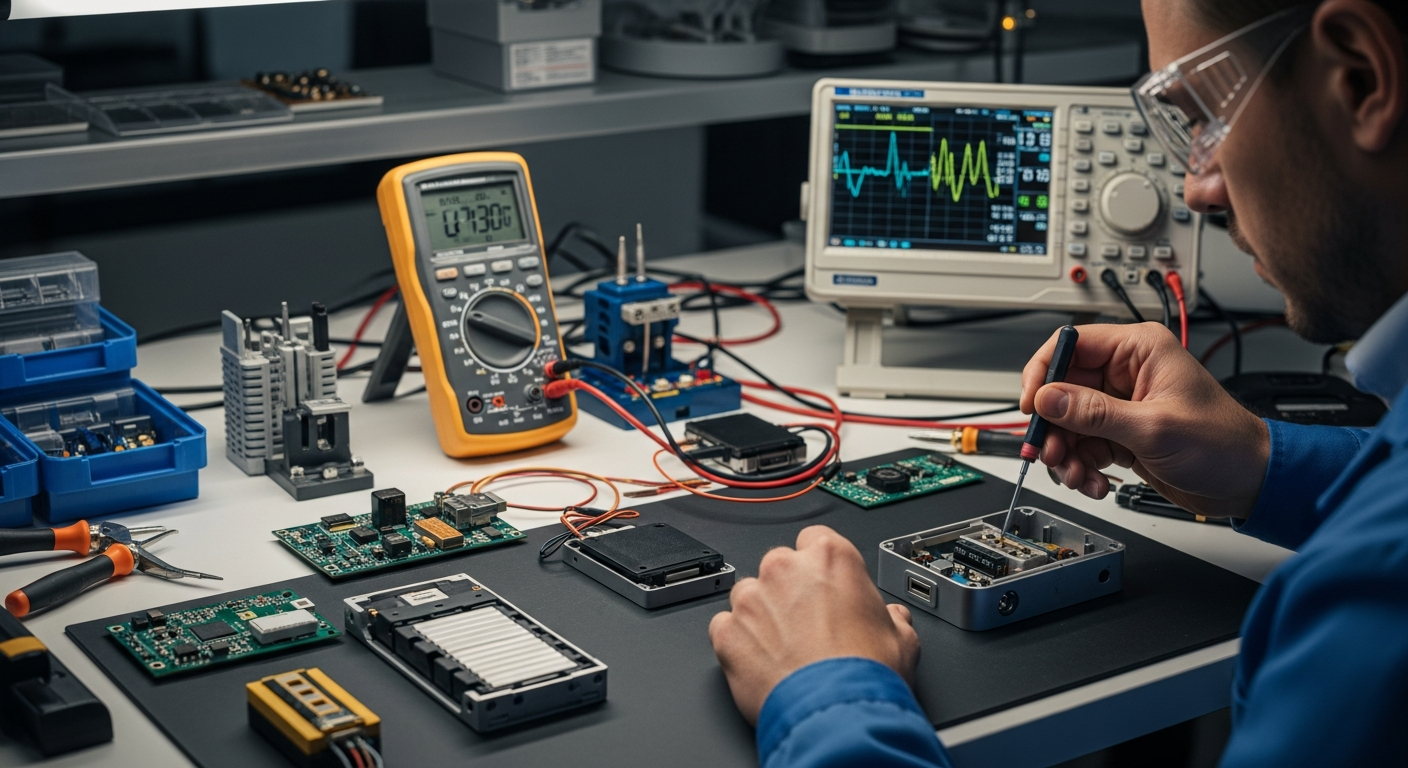
Precision Engineering for Automotive Engines and Systems
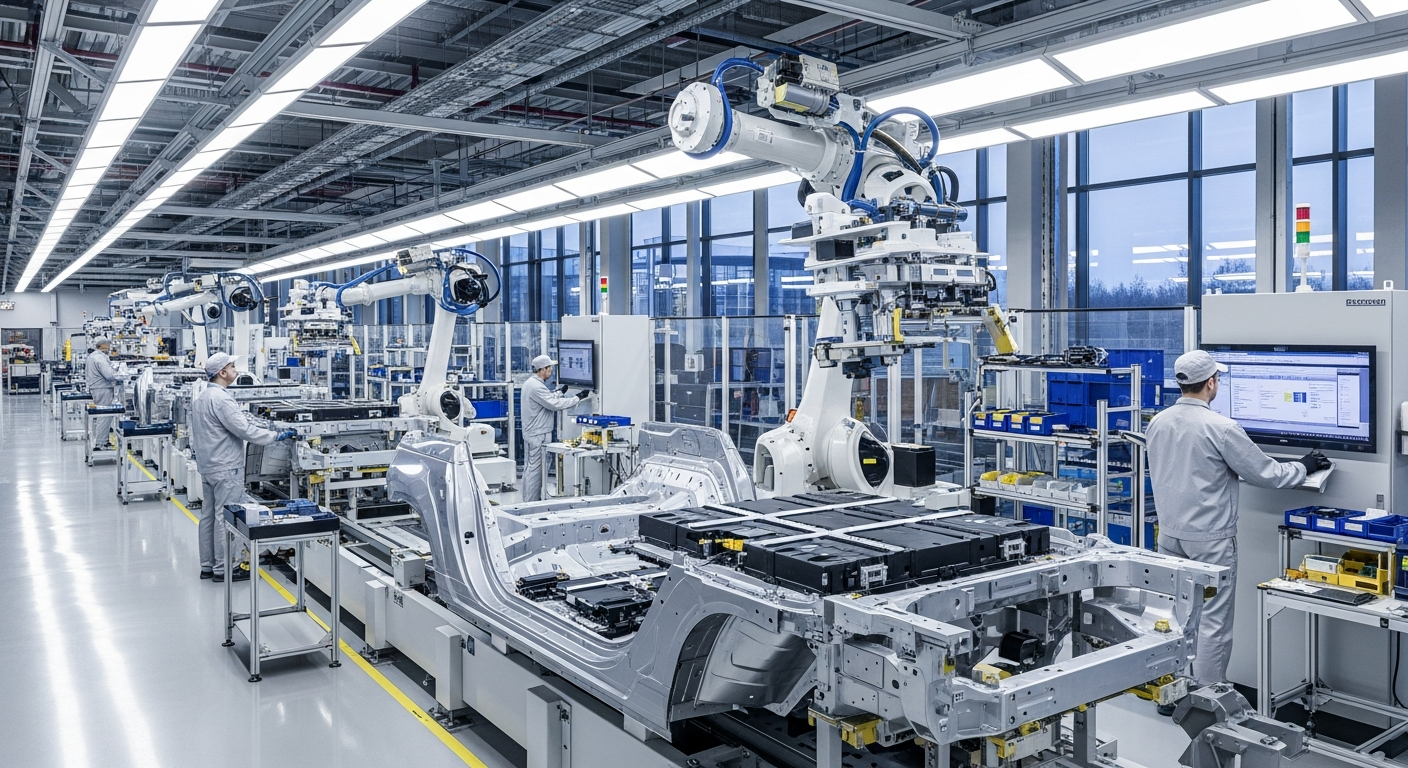
The manufacturing of automotive engines, transmissions, and other critical mechanical systems demands exceptional precision. This process often begins with raw materials like various metal alloys, which are then cast, forged, or machined into specific shapes. Computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) play a crucial role, ensuring that components meet exact specifications for fit and function. The internal workings of an engine, for instance, require tolerances often measured in micrometers to ensure optimal performance, fuel efficiency, and longevity. Advanced robotics and automation are widely used to achieve the consistency and accuracy required for mass production, reducing human error and increasing output.
Advanced Materials and Manufacturing for Wheels and Suspension
Wheels and suspension systems are fundamental to a vehicle’s handling, stability, and ride comfort. The manufacturing of these components involves selecting materials that offer an optimal balance of strength, weight, and durability. For wheels, this often includes aluminum alloys, which are cast or forged before undergoing heat treatment and machining. Suspension components, such as springs, shock absorbers, and control arms, can utilize high-strength steel or composite materials, depending on the vehicle’s design and intended use. Innovative manufacturing techniques, including hydroforming and advanced welding, are employed to create complex geometries that enhance both performance and safety across diverse road conditions.
Ensuring Safety and Durability in Component Production
Safety is paramount in automotive design and manufacturing. Every component, from brake systems to airbags, must meet stringent regulatory standards and undergo extensive testing. This focus on safety begins at the design stage, where engineers use simulation tools to predict how parts will behave under stress and in collision scenarios. During production, quality control measures are integrated at every step, utilizing sensors, cameras, and automated inspection systems to detect even minor flaws. Materials are selected not only for their immediate performance but also for their long-term durability and resistance to wear, corrosion, and fatigue, ensuring that vehicles remain reliable throughout their operational lifespan and contribute to overall road safety.
Integrating Technology for Electric and Hybrid Vehicle Components
The shift towards electric (EV) and hybrid vehicles has introduced new complexities and innovations in component manufacturing. Beyond traditional mechanical parts, the production now heavily involves advanced battery packs, electric motors, power electronics, and sophisticated control systems. Manufacturing battery cells, for example, requires cleanroom environments and highly specialized processes to ensure energy density and longevity. Electric motors demand precision winding and assembly, while power electronics involve intricate circuit board manufacturing and robust packaging to withstand automotive environments. These components are at the forefront of automotive technology, driving the industry’s evolution towards sustainable mobility and requiring continuous innovation in their production methods.
The Role of Design and Aerodynamics in Component Development
Automotive component manufacturing is not solely about mechanical function; design and aerodynamics play a significant role, influencing both aesthetics and performance. Components like exterior body panels, spoilers, and underbody elements are carefully shaped to minimize air resistance, which directly impacts a vehicle’s fuel efficiency or electric range and overall stability at speed. This involves extensive computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations and wind tunnel testing during the design phase. Manufacturing these parts often utilizes stamping, molding, and composite fabrication techniques, requiring high-precision tools and dies to achieve the exact contours and finishes specified by designers, blending form and function to enhance the driving experience.
Global Landscape of Automotive Component Manufacturing
The automotive component manufacturing sector is characterized by a global network of specialized suppliers. Companies such as Bosch, Continental, ZF Friedrichshafen, Denso, and Magna International are prominent examples of tier-one suppliers that provide a vast array of components, from complete powertrain systems and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) to interior modules and chassis parts. These manufacturers often operate extensive research and development facilities, continuously innovating to meet the evolving demands of vehicle manufacturers and regulatory requirements. Their production facilities are strategically located worldwide, enabling efficient supply chains that support the global automotive industry’s massive scale of transport and vehicle assembly.
Automotive component manufacturing is a dynamic and multifaceted field, continuously evolving with technological advancements and shifting industry demands. From the initial design and material selection to precision engineering and rigorous quality control, each stage ensures that vehicles are built to exacting standards for performance, safety, and efficiency. The integration of advanced manufacturing techniques and a commitment to innovation are key drivers in shaping the future of mobility.