Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems Explained
Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) represent a significant evolution in vehicle technology, designed to enhance the safety and convenience of driving. These systems utilize a range of sensors, cameras, and software to perceive the driving environment, analyze potential risks, and assist drivers in various scenarios, from preventing collisions to easing the burden of long-distance travel. Understanding the core functionalities and underlying principles of ADAS is key to appreciating their growing role in modern vehicles and the future of transportation.
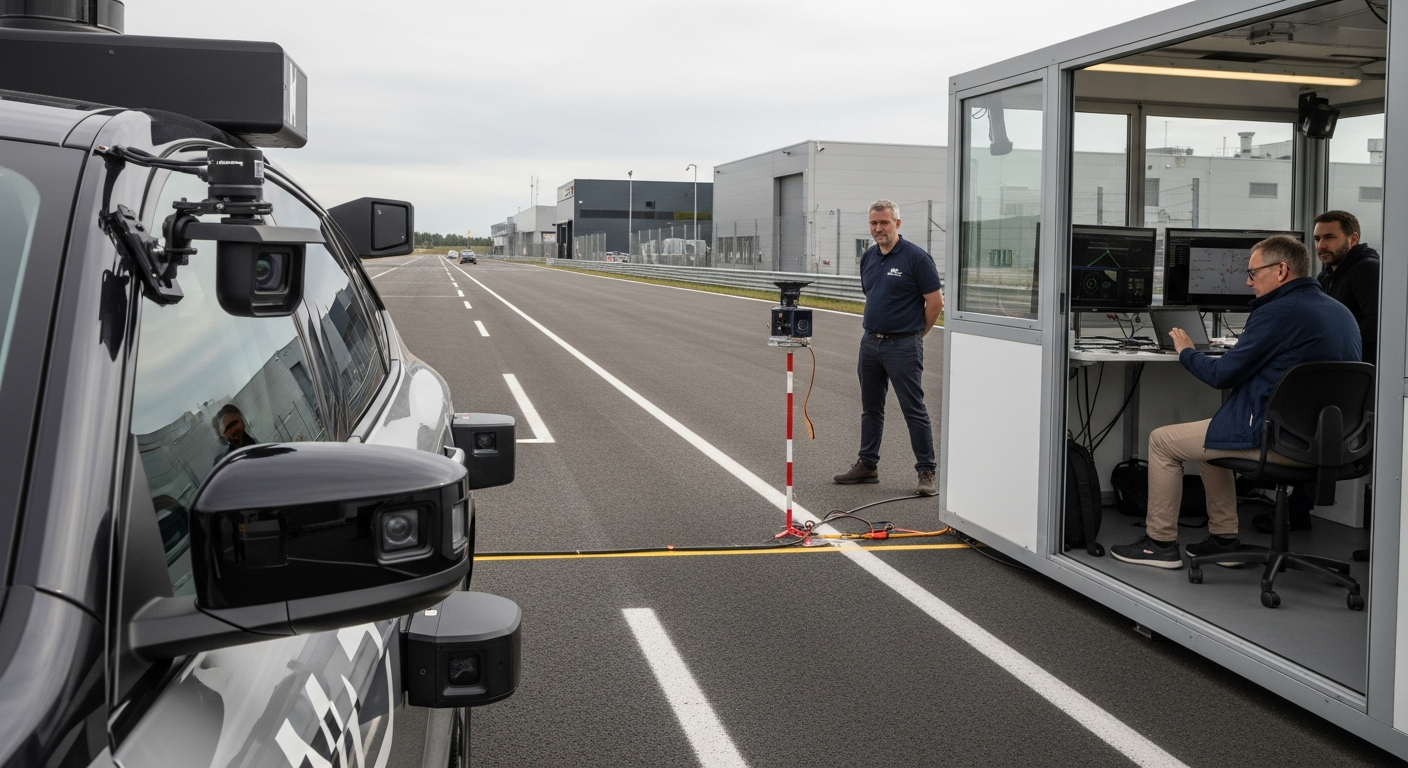

Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) are increasingly becoming standard features in contemporary vehicles, fundamentally changing the driving experience. These systems integrate various technologies to support the driver, improve vehicle safety, and potentially mitigate the severity of accidents. By leveraging sophisticated sensors and real-time data processing, ADAS features provide alerts, intervene when necessary, or automate certain driving tasks, thereby reducing driver fatigue and enhancing overall road safety.
How Do ADAS Features Enhance Vehicle Safety?
Vehicle safety is a primary driver behind the development and implementation of ADAS. Features such as Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB), Lane Keeping Assist (LKA), and Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) are designed to prevent or reduce the impact of collisions. AEB systems use radar and cameras to detect obstacles and apply brakes if the driver does not react in time. LKA helps keep the vehicle within its lane through gentle steering corrections, while ACC maintains a set speed and a safe following distance from the vehicle ahead. These systems contribute significantly to passive and active safety measures, working in tandem with traditional safety features like airbags and seatbelts to protect occupants. The continuous refinement of these technologies leverages advancements in sensor technology and processing power, making vehicles more adept at perceiving and reacting to complex driving situations.
The Role of Connectivity and Telematics in ADAS
Connectivity and telematics play a crucial role in the evolution and effectiveness of ADAS. Modern vehicles are often equipped with embedded connectivity modules that allow them to communicate with external networks, other vehicles (V2V), and infrastructure (V2I). This enables features like real-time traffic updates, remote diagnostics, and over-the-air (OTA) software updates for ADAS components. Telematics systems can also collect data on driving behavior, which can be used to further refine assistance algorithms and personalize the driving experience. The integration of robust cybersecurity measures is paramount to protect these connected systems from unauthorized access and ensure the integrity of the data exchanged, safeguarding both vehicle functionality and driver privacy. This interconnected ecosystem is vital for the development of more sophisticated autonomous driving capabilities.
Engineering and Production of ADAS Components
The engineering and production of ADAS components require precision and advanced manufacturing techniques. Developing the sensors—such as radar, lidar, ultrasonic, and cameras—along with the electronic control units (ECUs) and software that process the data, involves complex engineering challenges. Material selection is critical for components that must withstand varying environmental conditions, from extreme temperatures to vibrations. The manufacturing process must ensure high reliability and consistency, as any malfunction in these safety-critical systems could have serious consequences. This also extends to the integration of these systems into the overall vehicle architecture, including considerations for different propulsion types like electric and hybrid vehicles, where power management and electromagnetic compatibility are key factors. Continuous testing and validation are essential throughout the production lifecycle to meet stringent safety standards and ensure optimal performance.
ADAS and the Future of Urban Mobility
ADAS technologies are instrumental in shaping the future of urban mobility. As cities become more densely populated, the demand for safer and more efficient transportation solutions grows. ADAS features contribute to reducing human error, which is a major cause of accidents, thereby making urban environments safer for pedestrians, cyclists, and drivers alike. Furthermore, the advancements in driver assistance are a stepping stone towards higher levels of autonomous driving, which promises to revolutionize how people navigate urban landscapes. From smart parking assistance to traffic jam assist features, ADAS helps mitigate the stresses of urban driving. The development of electric vehicles, with their often-integrated advanced digital platforms, further accelerates the adoption and sophistication of ADAS, contributing to a vision of more sustainable and intelligent urban transportation systems. The ongoing research in areas like vehicle aerodynamics and tire technology also considers how these elements interact with ADAS for optimal performance and efficiency.
Understanding the Costs of ADAS Technology
While specific costs for ADAS features vary widely, they typically add to the overall price of a vehicle, either as standard equipment on higher trims or as optional packages. The cost can depend on the complexity and number of features included. For instance, a basic package might include rear parking sensors and a rearview camera, while a premium package could offer adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assist, and automatic emergency braking. These systems involve expensive hardware like radar sensors and sophisticated cameras, alongside the software development and integration costs. As technology matures and production scales, the cost of individual ADAS components tends to decrease, making these features more accessible across a broader range of vehicles. However, the continuous innovation means that new, more advanced systems are always under development, often commanding a premium initially. Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
| Feature/System | Provider (Example) | Cost Estimation (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Basic ADAS Package (e.g., AEB, LKA) | Mainstream Automaker | $500 - $2,000 (as part of trim/package) |
| Advanced ADAS Package (e.g., ACC, Traffic Jam Assist) | Premium Automaker | $2,000 - $5,000 (as optional package) |
| Parking Assist System | Various Brands | $300 - $1,000 (standalone option) |
| Blind Spot Monitoring | General Automaker | $200 - $800 (often bundled) |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
The Role of Driver Assistance in the Evolution of Autonomous Systems
Driver assistance systems are foundational to the development of fully autonomous vehicles. Each ADAS feature represents a step towards automating specific driving tasks, gradually building the technological and regulatory framework required for self-driving cars. The progression from Level 0 (no automation) to Level 5 (full automation) as defined by the SAE International standards relies heavily on the capabilities developed within ADAS. Features like adaptive cruise control with stop-and-go functionality and lane centering are examples of Level 2 automation, where the vehicle can control both steering and acceleration/deceleration under driver supervision. The continued evolution of these systems, including enhanced sensor fusion, artificial intelligence, and real-time mapping, is crucial for overcoming the complexities of real-world driving environments and achieving reliable autonomous operation. This journey involves significant investment in engineering, research, and development to ensure both safety and efficiency.
Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems are transforming the automotive landscape by significantly improving vehicle safety, enhancing driving convenience, and laying the groundwork for future autonomous vehicles. As these technologies continue to evolve, they promise to make transportation safer, more efficient, and more integrated into our daily lives, influencing everything from urban planning to individual mobility choices. The ongoing advancements in engineering, connectivity, and manufacturing will ensure that ADAS remains a critical area of innovation in the automotive industry.