The Advancement of Telemedicine Through Telecommunication
Healthcare, like many other sectors, has greatly benefitted from advancements in telecommunications. This marriage of technology and medicine has given birth to telemedicine, a rapidly growing field that is reshaping healthcare delivery worldwide. Telemedicine is the distribution of health-related services and information via electronic information and telecommunication technologies. It allows long-distance patient care, advice, reminders, education, intervention, and remote admissions. The inception of telemedicine can be traced back to the early 20th century when electrocardiograph data were transmitted over telephone wires. However, the development and proliferation of the internet and related technologies have significantly accelerated the growth and potential of telemedicine.
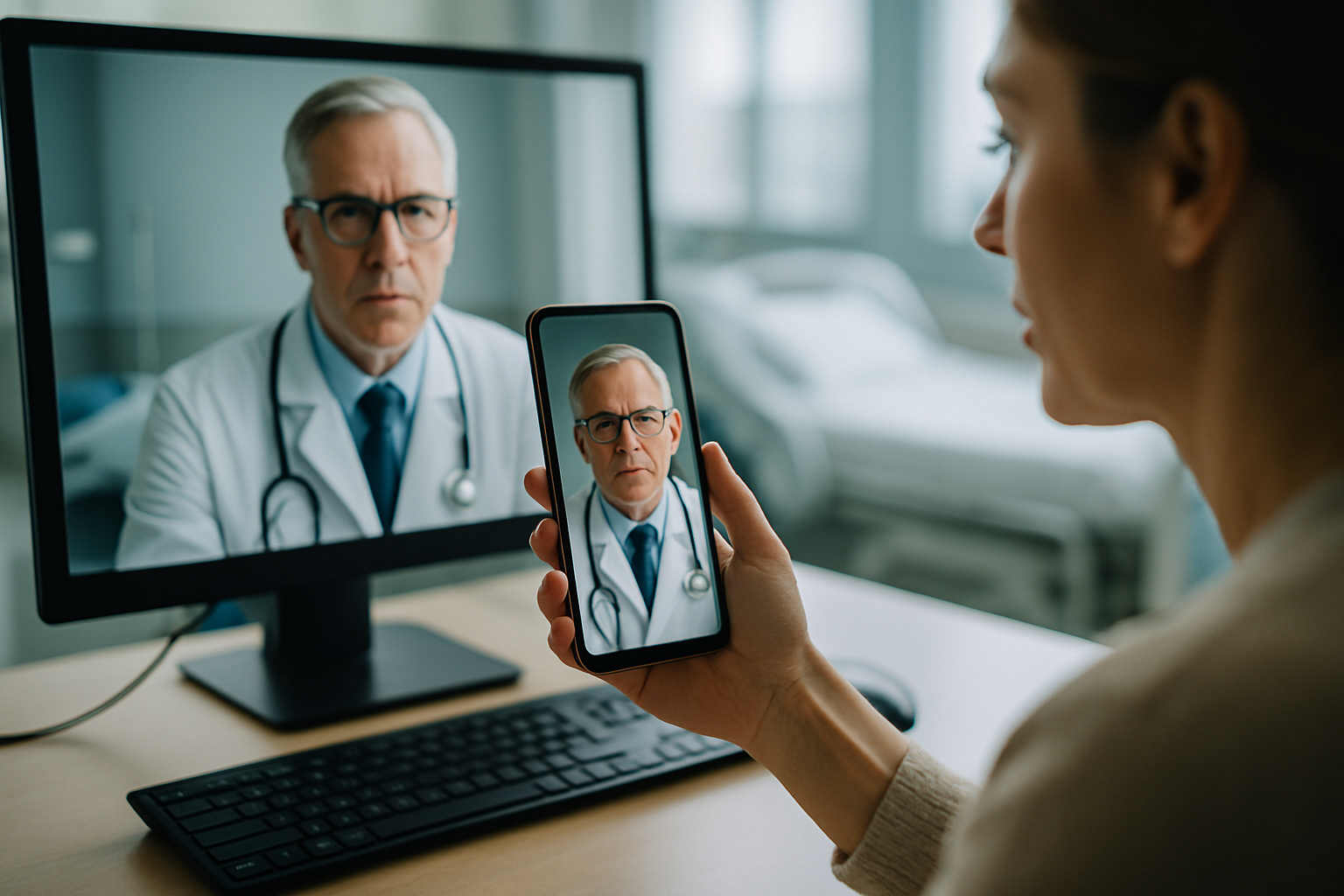

Current Trends and Regulatory Changes in Telemedicine
Currently, telemedicine is experiencing a surge in usage, largely driven by the COVID-19 pandemic. With social distancing measures in place, healthcare providers are turning to telemedicine to continue providing care to their patients remotely. This has been made possible by regulatory changes that have relaxed some of the restrictions on telemedicine. For instance, the U.S. federal government has expanded access to telehealth services for Medicare patients, and many private insurers have followed suit.
The Impact of Telemedicine on Healthcare Delivery
Telemedicine has a profound impact on healthcare delivery. Firstly, it provides access to medical services for individuals in remote locations or those with mobility issues. Secondly, it reduces the strain on healthcare facilities by allowing healthcare providers to assess and treat minor ailments remotely, thus freeing up resources for more critical cases. Thirdly, it enhances continuity of care by making it easier for patients to schedule follow-up appointments and maintain regular contact with their healthcare providers.
The Challenges and Practical Applications of Telemedicine
Despite its numerous benefits, telemedicine comes with its fair share of challenges. These include issues related to data security, patient privacy, and the risk of misdiagnosis due to the lack of physical examination. Moreover, not all health issues can be addressed through telemedicine. However, it has proved particularly useful in certain fields such as radiology, psychiatry, and chronic disease management.
The Future of Telemedicine
Research shows that telemedicine is here to stay. As the technology improves and the regulatory landscape evolves, telemedicine will become an increasingly integral part of healthcare delivery. The potential applications are vast, from remote patient monitoring and virtual consultations to AI-driven diagnostics and personalized treatment plans.
In conclusion, the advancement of telemedicine through telecommunications is a testament to how technology can transform industries. By overcoming geographical and logistical barriers, telemedicine has the potential to make healthcare more accessible, efficient, and patient-centered. However, for its full potential to be realized, the challenges it presents must be addressed strategically.