Legal frameworks for property transactions
Understanding the legal frameworks governing property transactions is essential for anyone involved in buying, selling, or investing in real estate. These regulations provide structure, protect rights, and ensure transparency across diverse property types, from residential homes to large-scale commercial developments. Navigating these legal landscapes requires awareness of local and international laws, contractual obligations, and the roles of various stakeholders.
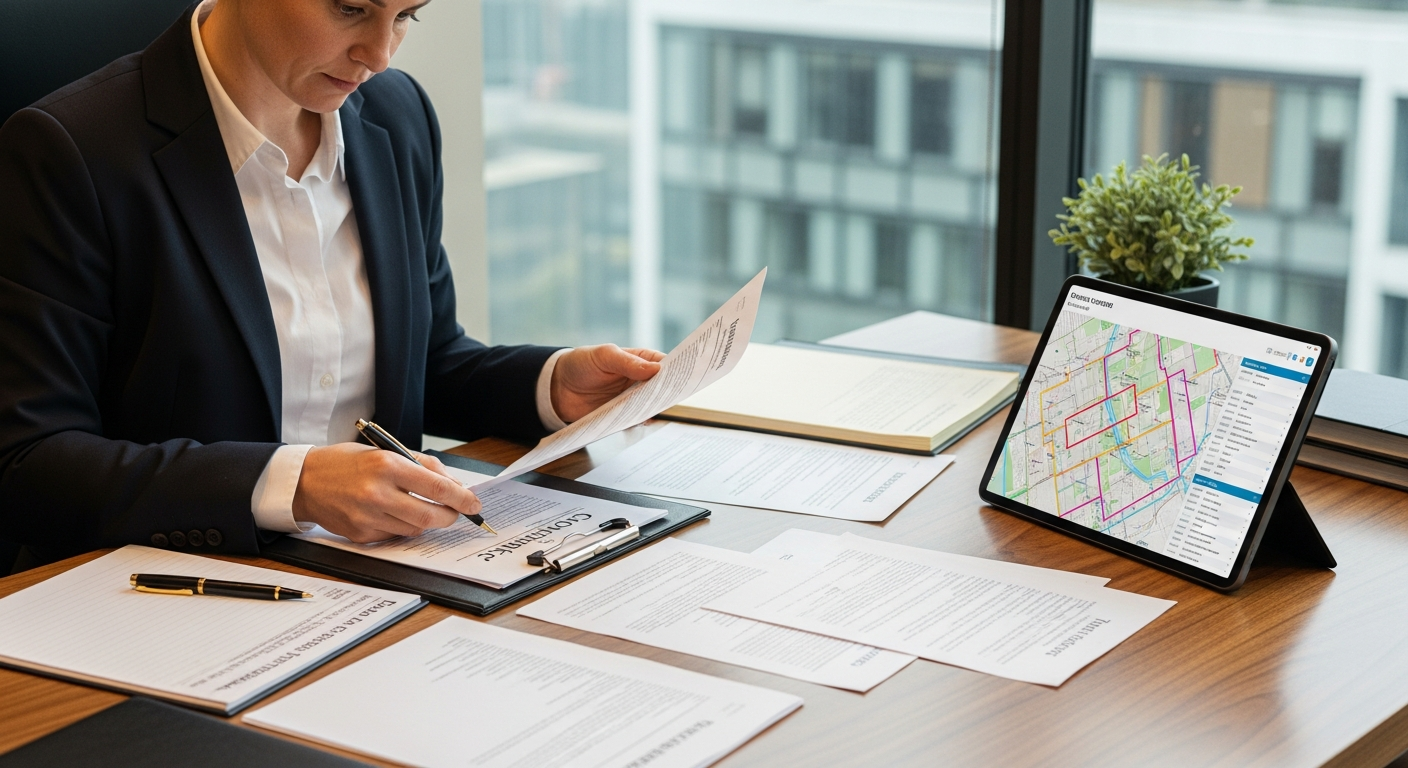

The acquisition and disposition of property, whether land, housing, or commercial buildings, are complex processes underpinned by extensive legal frameworks. These regulations vary significantly across jurisdictions, reflecting different historical, cultural, and economic contexts. A clear understanding of these legal foundations is crucial for ensuring secure and legitimate transactions, minimizing risks, and protecting the interests of all parties involved in the real estate market.
Understanding Property Ownership and its Legal Implications
Property ownership defines the rights and responsibilities associated with possessing real assets. Legally, ownership can manifest in various forms, such as freehold, leasehold, or commonhold, each with distinct implications for control, duration, and transferability. The legal framework establishes how ownership is proven, typically through deeds and registration systems, and outlines the rights of an owner to use, occupy, improve, or transfer their property. It also addresses easements, covenants, and other encumbrances that can affect a property’s value and usability, making due diligence a critical step in any acquisition.
Regulatory Aspects of Land and Building Transactions
Transactions involving land and buildings are subject to a multitude of regulatory aspects designed to ensure orderly development and protect public interest. These include zoning laws that dictate permissible land use, building codes that set construction standards for new development, and environmental regulations that govern land remediation and sustainable practices. The process of acquiring property often involves obtaining various permits and approvals, ensuring compliance with local planning authorities, and adhering to strict legal procedures for transferring title, which can involve conveyancing solicitors or notaries.
Legal Considerations for Residential and Commercial Real Estate
Residential and commercial real estate transactions, while both falling under the umbrella of property law, often have distinct legal considerations. Residential property transactions are typically more focused on consumer protection, disclosure requirements, and the rights of individual homeowners. Commercial property investment, on the other hand, often involves more complex contracts, detailed lease agreements, and considerations related to business operations, tax implications, and the specific needs of tenants or occupants. The scale and nature of assets in commercial dealings also necessitate a different approach to finance and risk assessment.
The Role of Finance and Valuation in Property Acquisition
Finance plays a pivotal role in property acquisition, with legal frameworks governing mortgages, loans, and other forms of real estate financing. Lenders require legally sound collateral, and the terms of financing agreements are subject to consumer protection laws and financial regulations. Property valuation, while often an economic assessment, also has legal implications, particularly in areas like taxation, insurance, and eminent domain, where fair market value is legally determined. Independent valuations are often a prerequisite for securing finance and are crucial for informed investment decisions.
Navigating Global and Urban Real Estate Markets Legally
Global and urban real estate markets present unique legal challenges due to their international scope and high density. Cross-border property investment involves navigating international treaties, foreign ownership restrictions, and different legal systems for property registration and taxation. Within urban areas, legal frameworks address issues like urban planning, heritage protection, compulsory purchase orders for infrastructure development, and regulations concerning multi-unit dwellings. Understanding these specific legal nuances is vital for successful acquisition and development in diverse market environments.
Future Trends and Sustainability in Property Law
The real estate market is continuously evolving, and legal frameworks are adapting to incorporate new trends and sustainability goals. This includes laws promoting green building standards, energy efficiency, and renewable energy installations in buildings. Technology also influences property law, with discussions around digital land registries, smart contracts for transactions, and the legal implications of proptech innovations. These developments aim to make property transactions more efficient, transparent, and environmentally responsible, shaping the future of property ownership and development.