Health and Wellness Through Varied Cuisines
Exploring the diverse world of culinary traditions reveals a profound connection between what we eat and our overall well-being. Each cuisine offers unique approaches to ingredients, preparation methods, and meal structures, contributing to a holistic understanding of health. From the vibrant spices of Asian dishes to the hearty grains of European gastronomy, the global pantry provides an abundance of options to support a balanced and nutritious lifestyle, emphasizing that wellness is a journey enriched by culinary exploration.
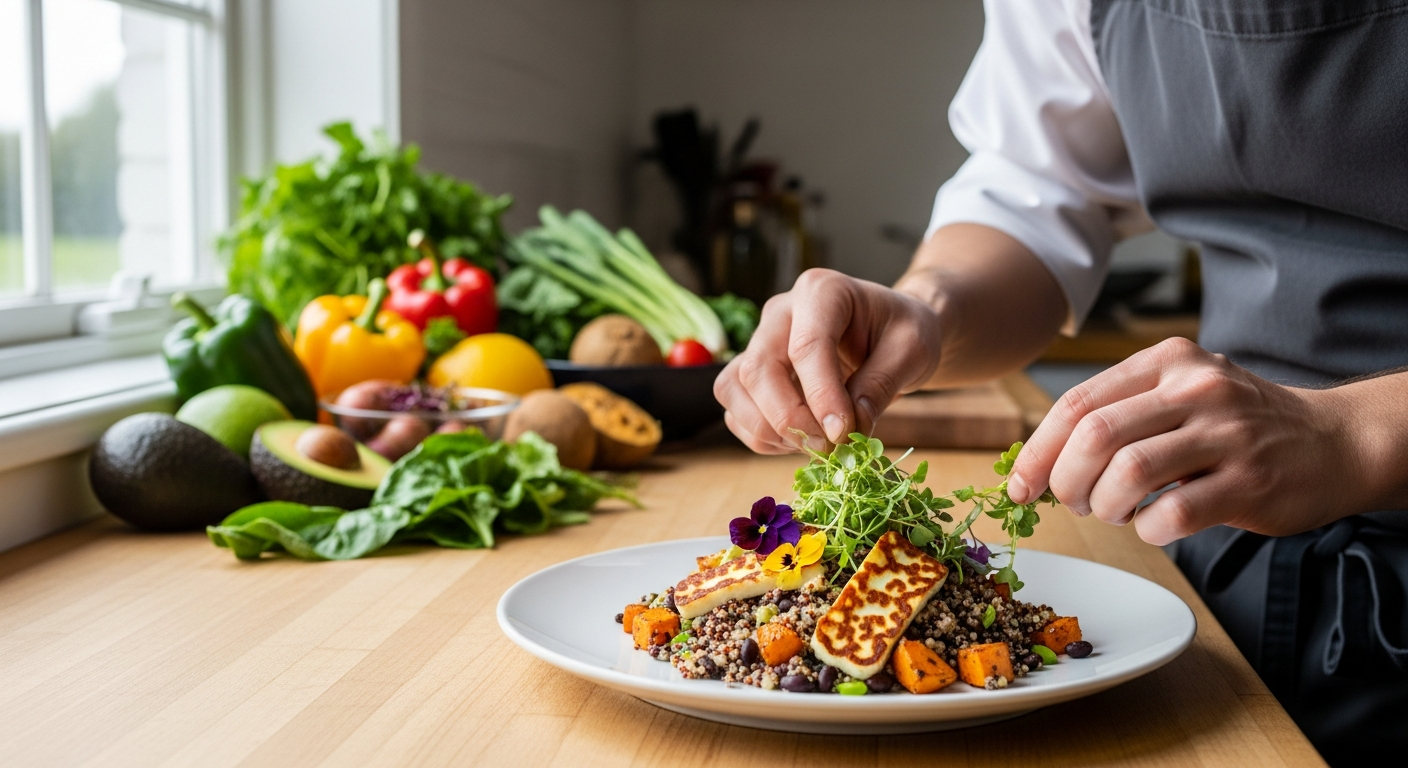

The global landscape of food is a tapestry woven with countless culinary traditions, each reflecting the history, environment, and values of its people. Understanding these varied cuisines goes beyond mere taste; it delves into the core of how different cultures approach sustenance, health, and social connection. Gastronomy, the art and science of good eating, highlights the importance of quality ingredients, thoughtful preparation, and the communal experience of meals, all of which play a role in promoting overall wellness.
Exploring Diverse Culinary Traditions and Their Cultural Roots
Cuisine is deeply intertwined with culture, offering insights into regional agricultural practices, historical trade routes, and societal customs. From the Mediterranean diet, rich in olive oil, fresh produce, and lean proteins, to the plant-forward traditions of many Asian cultures, the world showcases a spectrum of eating patterns. These diverse approaches often prioritize seasonal produce and local ingredients, fostering a connection to the environment and traditional methods of food preparation. Learning about global food traditions can inspire new ways of thinking about our own diets and how to incorporate a broader range of flavors and textures into daily eating.
The Nutritional Landscape of Global Ingredients and Health Benefits
At the heart of any healthy diet are the ingredients themselves. Varied cuisines introduce a wide array of produce, grains, legumes, and proteins, each contributing unique nutritional profiles. For instance, the emphasis on fermented foods in some East Asian diets provides probiotics beneficial for gut health, while the generous use of herbs and spices across many cultures adds antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds. Understanding the specific health benefits associated with different ingredients, such as omega-3 fatty acids in fish from Nordic diets or the fiber in whole grains prevalent in many European diets, allows for informed dietary choices that support long-term wellness. A balanced diet, drawing from the strengths of various global food sources, can provide essential vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients.
Culinary Techniques and the Art of Balanced Meals
Beyond ingredients, the way food is prepared significantly impacts its nutritional value and palatability. Traditional culinary techniques, honed over centuries, often prioritize methods that preserve nutrients and enhance flavors naturally. Steaming, stir-frying, and baking, common in many global kitchens, are examples of methods that can reduce the need for excessive fats while locking in the goodness of the produce. The structure of meals also varies, with some cultures favoring multiple small dishes that encourage mindful eating and diverse nutrient intake, while others focus on a single, substantial main course. Adopting varied preparation methods and meal compositions can lead to more satisfying and nutritionally complete eating experiences.
The Role of Beverages and Sustainable Eating Practices
Beverages are an integral part of global gastronomy, extending beyond simple hydration to cultural rituals and nutritional contributions. From green tea in Japan, known for its antioxidant properties, to various herbal infusions enjoyed worldwide, drinks often complement meals and offer their own health advantages. Contemporary trends in food also increasingly focus on sustainability, encouraging choices that are good for both personal health and the planet. This includes prioritizing local produce, reducing food waste, and supporting ethical sourcing of ingredients. Integrating these sustainable eating practices into our daily lives aligns with a holistic view of health and contributes to a more responsible global food system.
Conclusion
Embracing the diversity of global cuisines offers a rich pathway to enhancing health and wellness. By exploring new ingredients, understanding varied preparation methods, and appreciating the cultural significance of food, individuals can broaden their palates and enrich their diets. The journey through international flavors and culinary traditions not only makes eating more enjoyable but also provides a comprehensive framework for nourishing the body and mind, fostering a deeper connection to food and its profound impact on our lives.