Exploring the Ethics of Pet Ownership Responsibilities
Pet ownership is a deeply rewarding experience, offering companionship and joy to millions worldwide. However, it also entails a profound set of ethical responsibilities that extend beyond simply providing food and shelter. Understanding these obligations is crucial for ensuring the welfare of domestic animals and fostering a harmonious relationship between humans and their animal companions. This article delves into the various ethical considerations inherent in owning pets, from their initial acquisition to their lifelong care and impact on the broader environment.
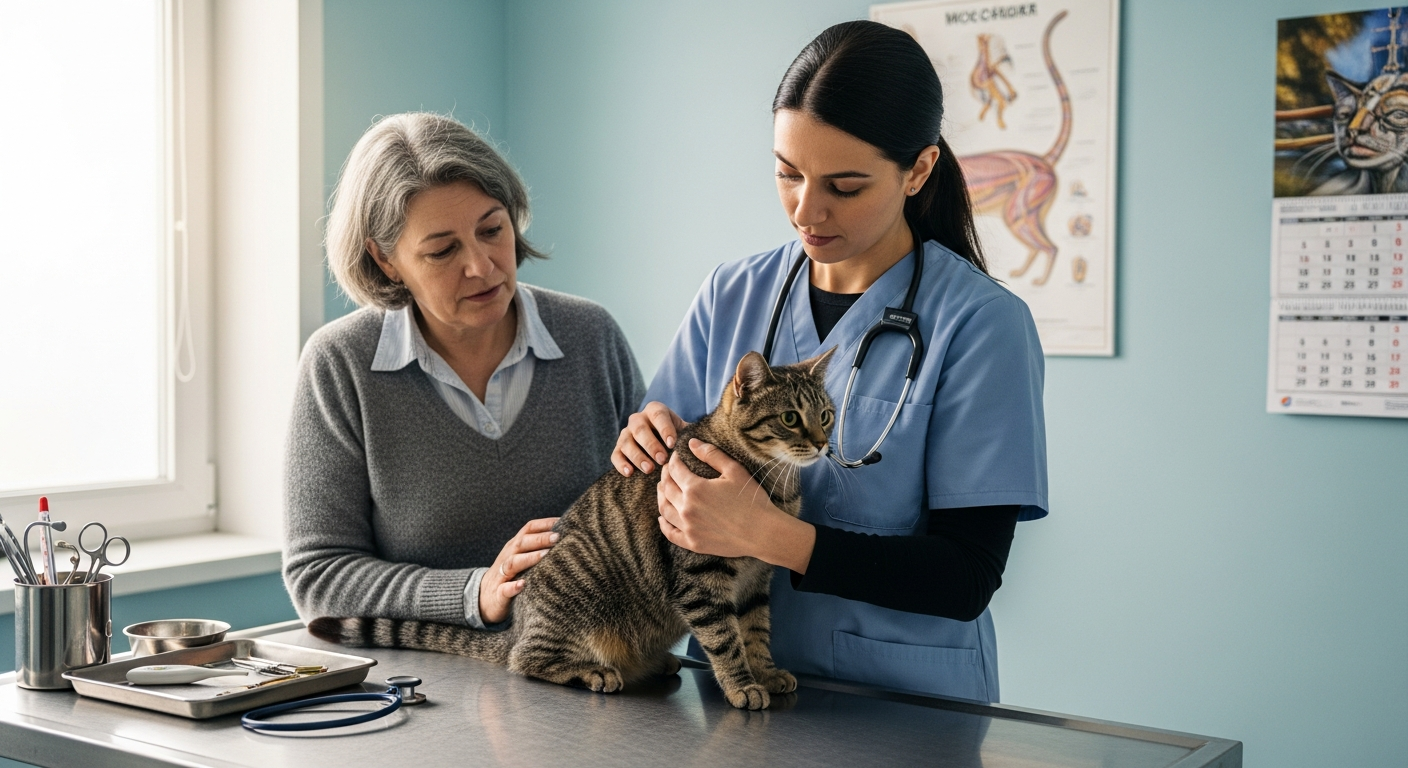

The decision to bring an animal into one’s home carries significant ethical weight. It signifies a commitment to providing a life of quality, respect, and dignity for a dependent creature. Ethical pet ownership encompasses a wide array of duties, including ensuring physical health, mental well-being, and responsible integration into society. These responsibilities are not static; they evolve with our understanding of animal behavior, needs, and our collective impact on the natural world.
Understanding the Ethical Dimensions of Pet Ownership
Ethical pet ownership begins with a fundamental recognition of an animal’s sentience and inherent value. This perspective moves beyond viewing pets merely as property and instead acknowledges their capacity to feel pain, pleasure, fear, and joy. The ethical framework dictates that owners must prioritize their pet’s welfare, making decisions that consistently serve the animal’s best interests. This includes considering the long-term commitment required, the specific needs of the species, and the resources available to provide appropriate care throughout their entire lifespan.
Ensuring Pet Welfare and Comprehensive Care
Central to responsible pet ownership is the provision of comprehensive care that supports an animal’s overall welfare. This involves meeting their basic physiological needs, such as appropriate nutrition and access to clean water, but also extends to creating a stimulating and safe environment. Adequate housing, regular exercise tailored to the species and breed, and opportunities for mental enrichment are vital. Furthermore, understanding and responding to a pet’s natural behavior patterns helps prevent stress and promotes a healthy bond between the animal and its human companions.
The Importance of Responsible Pet Adoption and Rescue
Ethical considerations are paramount when acquiring a pet. Choosing adoption from animal shelters or reputable rescue organizations is often highlighted as a responsible approach, as it helps address the issue of pet overpopulation and gives a home to animals in need. When considering specific breeds or species, it’s important to research their typical health issues, behavioral traits, and specific care requirements to ensure a good match for one’s lifestyle. Avoiding impulsive decisions and supporting ethical breeding practices, where applicable, are also key components of responsible acquisition.
Addressing Pet Health and Nutrition Needs
Maintaining a pet’s health is a continuous ethical obligation. Regular veterinary check-ups, vaccinations, and prompt attention to any signs of illness or injury are essential for preventing suffering and ensuring a long, healthy life. Proper nutrition, tailored to the animal’s age, species, and activity level, plays a crucial role in preventative care and overall well-being. Owners are ethically bound to provide a diet that supports their pet’s specific biological requirements, often guided by veterinary advice.
The Role of Veterinary Care and Training in Pet Well-being
Beyond basic health, consistent veterinary care is fundamental. This includes preventative medicine, dental care, and appropriate medical interventions when necessary. Furthermore, ethical pet ownership often involves investing in training, especially for domestic species like dogs and cats. Training not only helps manage behavior, making pets better integrated into human society, but also provides mental stimulation and strengthens the bond between owner and animal. Positive reinforcement training methods are generally considered the most humane and effective, aligning with ethical treatment principles.
Considering the Environmental Impact of Domestic Animals
The ethical dimensions of pet ownership also extend to the environment. Responsible owners consider the ecological footprint of their domestic animals, from the sourcing of pet food to the disposal of waste. Preventing pets from impacting local wildlife, particularly through responsible containment and supervision, is a critical aspect of environmental ethics. Supporting conservation efforts and understanding how certain pet species might affect local habitats if they were to escape or be abandoned contributes to a broader ethical perspective on our relationship with animals and the natural world.
Pet ownership is a significant commitment that demands a comprehensive understanding of ethical responsibilities. By prioritizing an animal’s welfare, making informed decisions about acquisition and care, and considering the broader environmental implications, owners can ensure a fulfilling and respectful relationship with their animal companions while contributing positively to animal welfare globally.